Animal milk oligosaccharides: structural diversity, biological functions, and health relevance
Keywords:
Milk Oligosaccharides, Bioactivity, Fucosylation, Gut Health, Infant Nutrition, Functional Foods.Abstract
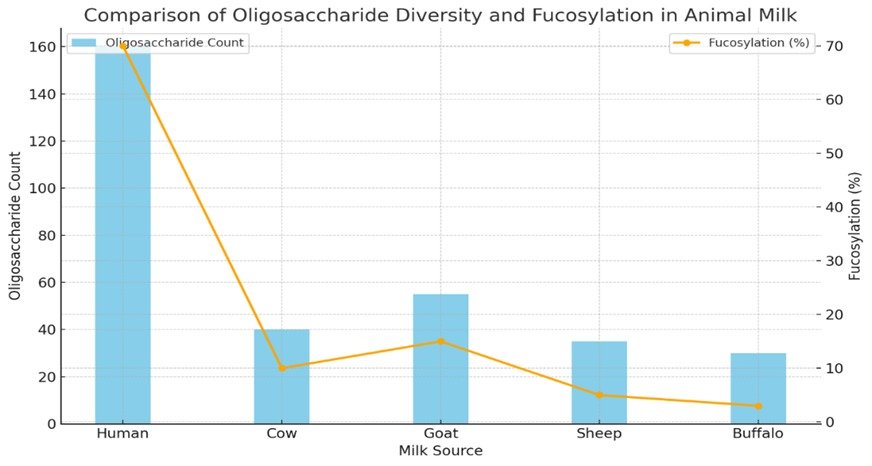
Plant-derived Milk oligosaccharides (MOs) are mammalian milk glycans with varied structure and high biological activity. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are well known for their prebiotic, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory functions, whereas animal milk oligosaccharides cow, goat, sheep, and buffalo are increasingly recognized for their health-promoting potential. This review summarizes and critically evaluates the existing scientific literature on animal-derived MOs' structure, biosynthesis, and healthy functions in animals, highlighting their similarities and differences with HMOs. With high-quality research paper sources, we discuss how bovine and caprine milk oligosaccharides contribute to a healthy gut, regulate immunity, and support its development. Comparative tabulation and visual inspection highlight the structural diversity and biological significance of animal-derived milk oligosaccharides for functional food and infant formula applications.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Apurwa Singh, Parinita Tripathy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




