Extent of impact of chemical fertilizers on soil pH
Keywords:
Chemical Fertilizer, Crops Productivity, Soil, pH, NPK, Urea.Abstract
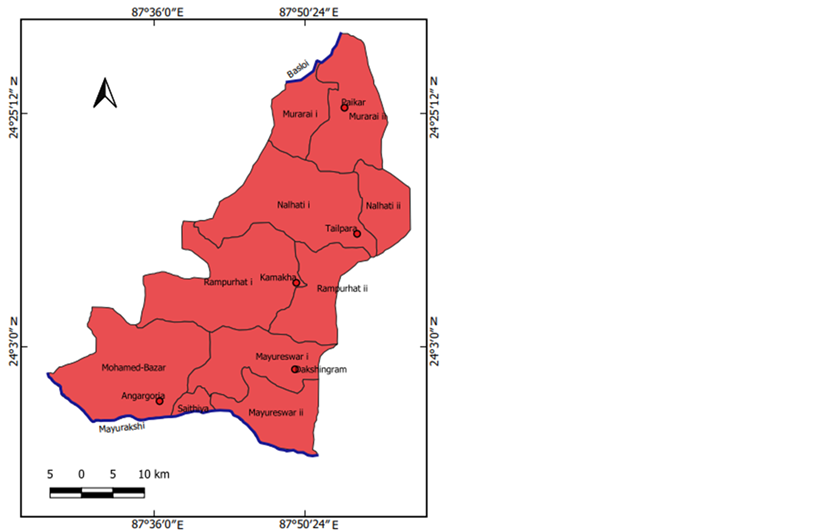
The objective of the present paper is to analyze the extent of the impact of the application of chemical fertilizers on the quality of soil, especially on the soil pH, in the interfluve of the Mayurakshi and the Basloi rivers in Birbhum district, West Bengal, India. The method used to conduct the study included a laboratory test of the soil samples, which was followed by a statistical analysis and interpretation. The soil samples have been collected in five different villages, namely Paikar, Tailpara, Kamakha, Dakshingram, and Md. bazaar, situated in different blocks in the district of Birbhum, where multi-cropping is practiced and different types of chemical fertilizers are used largely in agricultural operations. The result shows that long-term and continual application of chemical fertilizers, especially nitrogenous and urea fertilizers, to crop fields modifies the physical and chemical properties of the soil and decreases the level of soil pH. This makes the soil acidic. The reduction is more prominent where cultivation is practiced solely with chemical fertilizers, but very little or no such change in pH value is observed in the fields where farming is done by applying both chemical fertilizers and organic manures. To get rid of the problem, an integrated nutrient management system may be practiced to protect the soil from degradation and to maintain production.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. Lakshman Chandra Pal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




