Impact of women self-help groups on rural livelihoods in india: issues and challenges
Keywords:
Self-Help Women, Panchayats, Livelihoods, Social Awareness, Living Standards.Abstract
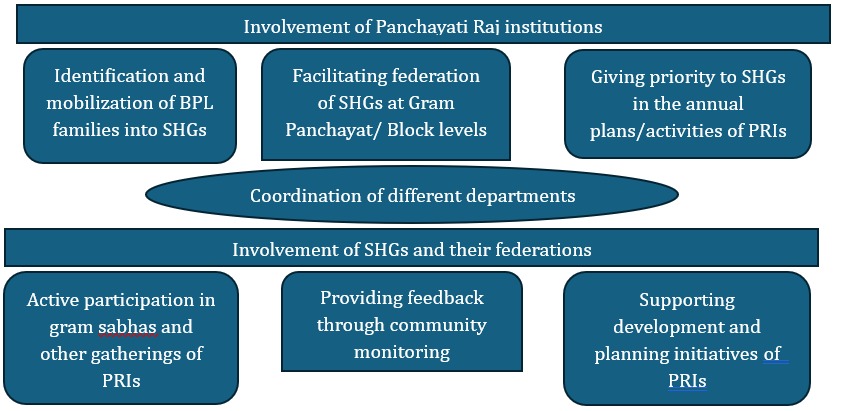
Countries across the world can achieve balanced development only when all their citizens are having equal participation in their endeavours for socio-economic growth. Countries with less gender gap are ahead on the path of development when countries having more gender gap in education and employment. It is already evident that women in developed countries are enjoying more socio-economic freedom when compared to women in developing countries. Indian government in her efforts to uplift the position of women has implemented numerous policies and programs since independence. Formation and continuation of SHGs was one among those programs with particular focus on rural women. Today, Self-help groups are considered to be the means for rural women empowerment. Since early 1980s, women SHGs, popularly known as DWACRA groups have been making a gradual progress towards empowerment in India. After joining SHGs, rural women have improved their living standards and gained access to multiple livelihoods opportunities, but they do face multiple challenges. Male chauvinistic environment, lack of marketing awareness for their products, lack of local political awareness, deprive SHG women of their basic rights of earning a decent living. The current study focuses on how women self-help groups are able to sustain their livelihood activities overcoming the societal challenges.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. Vasantha Gouri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
