Effect of spraying with colchicine alkaloid on seed viability of bread wheat varieties
Keywords:
Triticum Aestivum L, Genetic Compositions, Colchicine, Seed Vitality, Wheat Varieties.Abstract
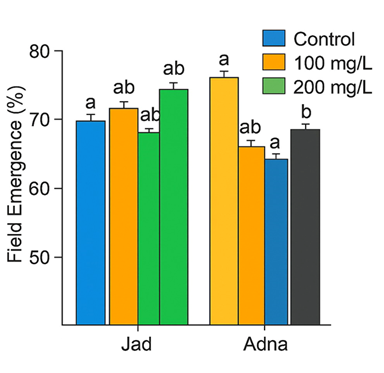
This study was conducted in the laboratories of the Seed Testing and Certification Department of Baqubah City in Diyala Governorate during the years 2022 and 2023, with the aim of studying the effect of the difference in the genetic composition of bread wheat and its response to spraying with colchicine alkaloid and its reflection on the vitality of its resulting seeds, as the experiment included two factors, the first is the varieties (Jad, Thariyah, Adna and Ibaa 99), and the second is spraying the vegetative group with colchicine alkaloid (at a concentration of 100 mg L-1 in one spray and at a concentration of 200 mg L-1 in two batches, each spraying half the amount) in addition to the comparison treatment (spraying with distilled water only). The experiment was applied using a completely randomized design (CRD) with three replicates. The results of the statistical analysis showed that wheat varieties had a significant effect on all studied traits, and the variety Ebaa 99 recorded the highest average for field emergence percentage (88.20%), seedling length (7.767 cm), dry radicle weight (47.34 mg) and dry seedling weight (50.92 mg). The results showed that spraying with colchicine alkaloid with an average of two sprays was significantly superior to the traits of field germination percentage (88.30%), seedling length (7.625 cm), radicle length (6.250 cm), dry radicle weight (47.90 mg) and dry seedling weight (50.03 mg). We conclude from this study that bread wheat varieties vary in seed vitality indicators, and the use of colchicine significantly improved these indicators, especially when using more than one spray.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




