Assessing the Potentials of Some Agro-Waste Peels Through Proximate Analysis
Keywords:
Agro-Waste Peels, Production Potentials, Bioethanol, Animal Feed, Substrates, Production Potential, Nutrients, Energy.Abstract
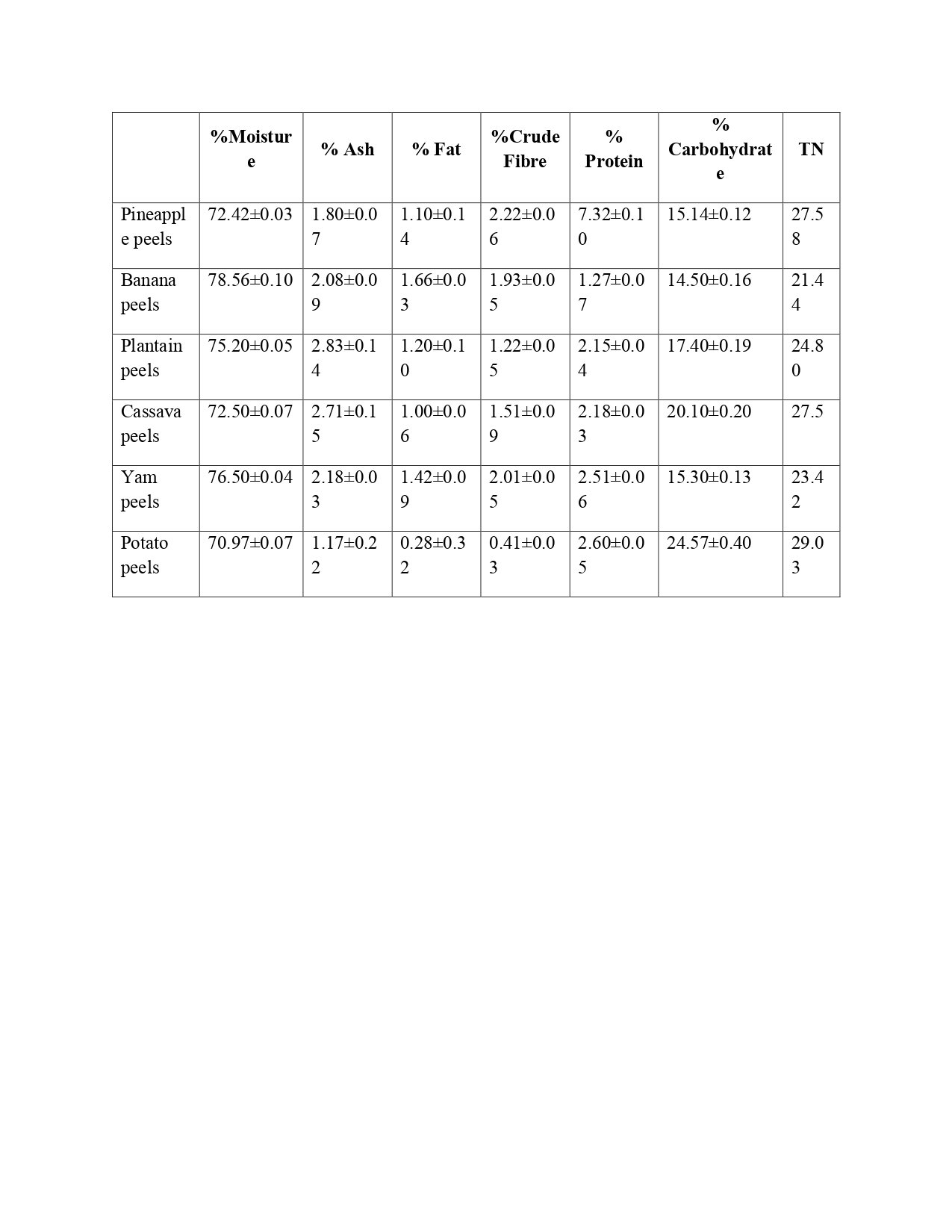
The economic potentials of some agro-waste peels were evaluated using proximate analysis. The substrates investigated were pineapple peels, banana peels, plantain peels, cassava peels, yam peels and potato peels. Their bioethanol production potentials were evaluated using their % carbohydrate content while their animal feed production potentials were evaluated using their total energy content on a dry weight bases. On comparative assessment, it was deduced that potato peels had the highest bioethanol production potential (84.64% carbohydrate content) while pineapple peels had the least (54.89% carbohydrate content). It was also deduced that potato peels had the highest animal feed production potential (383.04 Kcal/100g) while cassava peels had the least (356.84 Kcal/100g). Minerals were also found to be highest in plantain peels (11.41% ash) and cassava peels (9.85% ash). This research revealed that all the considered substrates were good sources of carbohydrates and energy when completely dried, although in varying degree.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




