Isolation of Bacteria from Milk Based Indian Sweets Sold in and Around Kolkata Using MPN Method
Keywords:
Sweets, Food Safety, Public Health, Quality, Vendors.Abstract
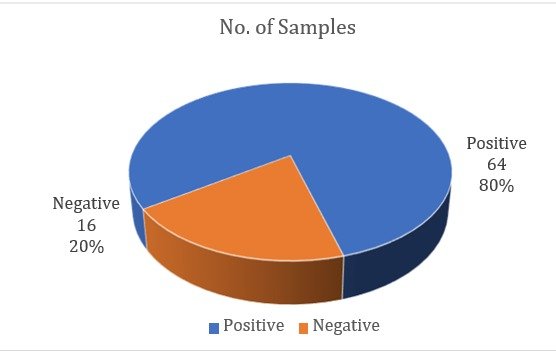
Milk is frequently used as a vital ingredient in the preparation of Indian sweets, which are renowned for their rich flavour and cultural significance. To guarantee consumer health, it is essential that these traditional treats are microbiologically safe. This study used the multiple tube test to evaluate the microbiological quality of milk- based Indian sweets sold in and around Kolkata. 80 samples in all were gathered, and the microbial contamination was examined. According to the findings, 64 of the 80 samples (or 80%) tested positively for different bacterial species. The identified bacterial strains included Acinetobacter baumannii (2.5%), Aeromonas schubertii (1.25%), Citrobacter freundii (2.5%), Citrobacter koseri (8.75%), Enterobacter cloacae (15%), Escherichia coli (12.5%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (2.5%), Klebsiella aerogenes (28.75%), and Klebsiella oxytoca (6.25%). The quality and safety of the region's milk-based Indian sweets are questioned by the presence of these pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria. The likelihood of foodborne infections linked to these sweets is shown by the prevalence of Enterobacteriaceae members. Since these traditional treats are prepared, stored, and distributed by regulatory agencies and sweet vendors, strict hygiene and quality control standards must be put in place.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Dr. Manoj Yogi, Dr. Sayan Bhattacharyya, Dr. Atul Raj, Amit Banik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




